View results
Display the freeze time and the temperature distribution on the plastic part and mold to locate regions where you can improve the cooling and optimize the cooling time.
-
Click Results to open the results page.
 The display window shows the global and local freeze time. The freeze time, or safe ejection time, is the duration for the plastic part to develop a thick enough solidified layer, enabling safe ejection while maintaining its integrity. The local freeze time is the time, in seconds, required for 20% of the local part thickness to drop below the safe ejection temperature. The global freeze time is the time, in seconds, required for 99% to 99.5% of the plastic to reach a safe temperature for ejection.
The display window shows the global and local freeze time. The freeze time, or safe ejection time, is the duration for the plastic part to develop a thick enough solidified layer, enabling safe ejection while maintaining its integrity. The local freeze time is the time, in seconds, required for 20% of the local part thickness to drop below the safe ejection temperature. The global freeze time is the time, in seconds, required for 99% to 99.5% of the plastic to reach a safe temperature for ejection.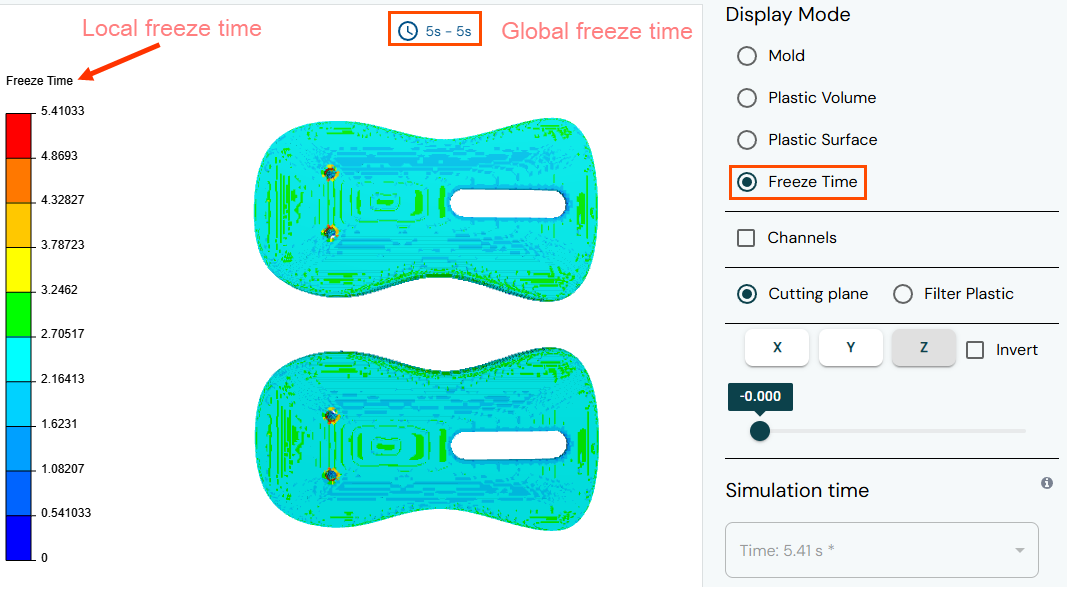
-
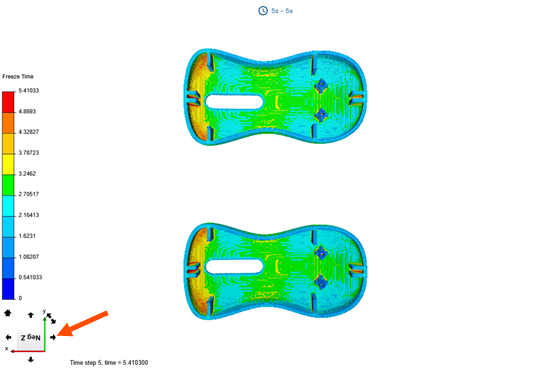
Rotate your model using the model manipulation tools to inspect the freeze time
distribution on your plastic part.
-
In the Display Mode panel, select the
Channels check box to display the channels
location.
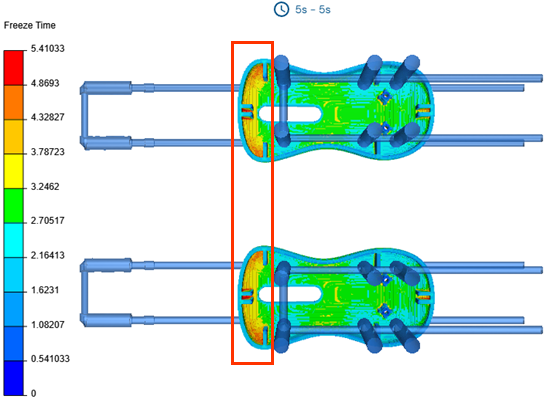 Notice that the highest freeze time regions are located at the curved sections of the mouse shell, where the cooling channels are relatively distant compared to the other side of the shell, leading to slower heat dissipation in these areas.
Notice that the highest freeze time regions are located at the curved sections of the mouse shell, where the cooling channels are relatively distant compared to the other side of the shell, leading to slower heat dissipation in these areas. - Clear the Channels check box to hide the channels location.
- From the Results list, select Plastic Surface to display the surface temperature distribution on the plastic part.
-
Select Filter Plastic, then move the slider to the
target cooling temperature. For example, 85 °C which is under the heat
deflection temperature of the material.
 The software displays areas of the plastic part where the temperature exceeds the value you specified with the slider. This helps you identify regions that require longer cooling to reach the target cooling temperature.
The software displays areas of the plastic part where the temperature exceeds the value you specified with the slider. This helps you identify regions that require longer cooling to reach the target cooling temperature. - From the Results list, select Mold to display the mold temperature distribution.
- Clear the Mold Group 1 check box to hide the mold cavity.
-
Rotate your model to inspect the temperature distribution in the mold
core.
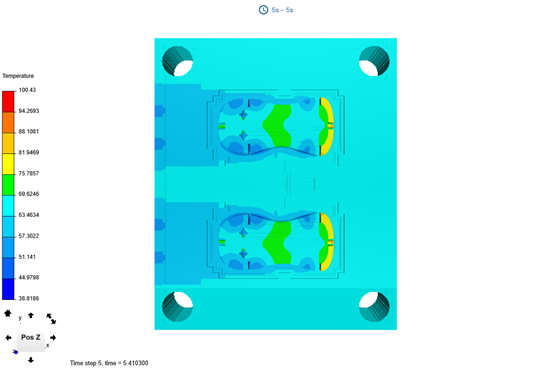 Notice that the temperature is highest on the front part of the mouse shell.
Notice that the temperature is highest on the front part of the mouse shell.
By analyzing the freeze time and temperature distribution, you can identify areas with inefficient cooling and adjust the cooling system accordingly. By optimizing cooling channels and ejection time, you can reduce cycle time, improve part quality, and enhance overall mold performance.
You have completed this tutorial. You can select another tutorial from the list on the left.
